The Australian Curriculum is said to be the national curriculum in Australia, which is followed by all primary and secondary schools. Its main purpose is to provide the best education to the students by introducing skills, understanding, and knowledge needed to work in this modern time.
Whenever needed, the curriculum is updated continuously to teach students what is valid and accurate. Moreover, the curriculum delivers education with the help of learning areas and general capabilities.
Aim of the Curriculum
The Australian Curriculum is focused on catering the needs of every student globally. It strongly advocates for inclusive education and firmly believes in the following principles:
- Every student can learn; their individual needs are equally important and hold significant value.
- Each student has the right to access knowledge as well as skills that serve as the building blocks for successful and continuous learning.
- It is important to establish high expectations for every student.
- The curriculum should be adjusted in a way that it can accommodate and recognize the diverse needs of students from different cultures.

The Australian Curriculum is designed to meet the needs of students worldwide
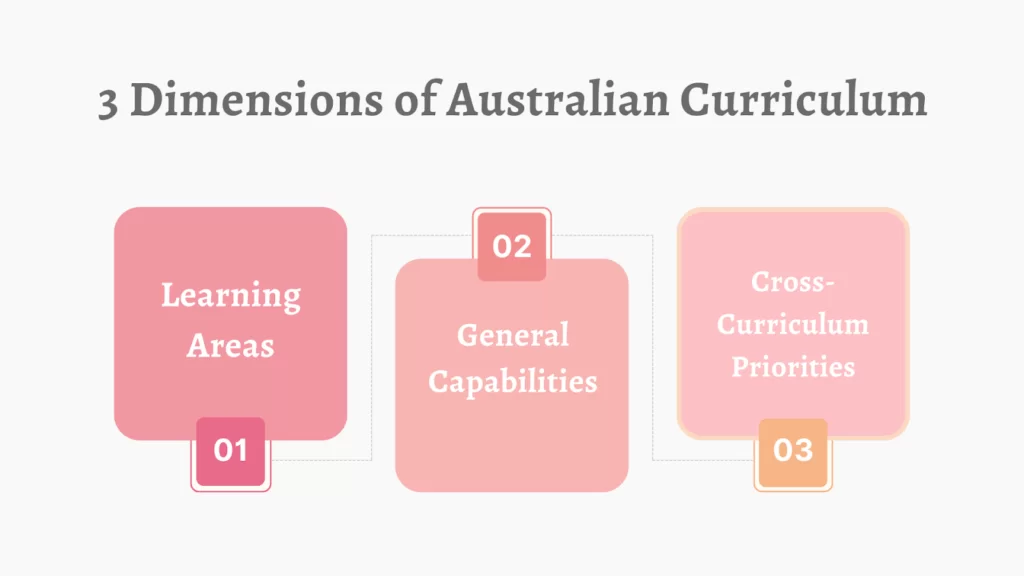
Three Dimensions of the Australian Curriculum
There are three dimensions in the Australian Curriculum:
- Learning Areas
- General Capabilities
- Cross-Curriculum Priorities
1. Learning Areas
The Australian Curriculum is divided into learning areas and subjects. The learning areas include humanities as well as social sciences. They include history, geography, civics, citizenship, economics, and Business. Apart from this, the arts include dance, drama, media arts, music, and visual arts. Moreover, the curriculum also includes technologies such as design and digital technologies. Lastly, you can choose from a diverse range of fifteen languages in order to enhance your knowledge and proficiency in a specific language that is different from your mother tongue.
2. General Capabilities
The Australian Curriculum contains a total of seven general capabilities, which aims to provide necessary skills and abilities to the younger generation of Australia in order to survive in the 21st century.
These general capabilities include:
- Literacy
- Critical and Creative Thinking
- Numeracy
- Personal and Social Capabilities
- Information and communication technology (ITC) capabilities
- Ethical Understanding
- Intercultural Understanding
3. Cross-Curriculum Priorities
In the Australian Curriculum, there are three priorities that are critical to Australia’s future. This specific dimension of the learning areas allows students to experience diverse contents of learning areas.
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander’s Histories and Culture
- Australia’s Engagement with Asia
- Sustainability
The Three dimensions offer teachers the flexibility to engage in personalized learning to meet the needs of individual students
Structure and Format
Typically, the students commence their learning journey by enrolling in kindergarten first. This marks the beginning of their 13-year educational journey that concludes with the attainment of the Higher School Certificate (HSC) upon the completion of Year 12. This prestigious certification enables students to seek admission to educational institutions worldwide.
The educational curriculum is structured around Eight Key Learning Areas (KLAs), which encompass English, mathematics, science, health and physical education, humanities, and social sciences, the arts, technologies, and languages.
1 English
English is an important language considered for young Australians. It includes subjects such as additional language or dialects, essential English, and literature.
3 Mathematics
Mathematics equips students with essential skills and knowledge for their development in their early years of education. It includes subjects such as specialist mathematics, general mathematics, mathematical methods, and essential mathematics.
3 Science
Science develops an understanding of practical concepts and processes among students and it includes subjects such as biology, chemistry, Earth and environmental science, and physics.
4 Humanity and Social Sciences
Humanity and social sciences includes 5 subjects. HASS (Australian Humanities and Social Science Curriculum), civics and citizenship, economics and business, geography, and history.
5 Arts
The arts have the ability to inspire and motivate students to think out of the box and embrace creativity . It includes dance, drama, media arts, music, and visual arts.
6 Technologies
In the Australian Curriculum, technologies play an important role in ensuring that all students benefit from understanding how technology works. It includes design and technologies and digital technologies.
7 Health and Physical Education
The curriculum of health and physical education provides certain types of learning opportunities that are contemporary, engaging, and relevant. It aims to equip students with the necessary skills, knowledge, and understanding of their physical health as well as mental health.
8 Languages
Languages are included in the Australian Curriculum to ensure that all students can actively participate in learning a language other than English. They include Arabic, German, Spanish, French, Japanese, Korean, Chinese, Hindi, and many more.
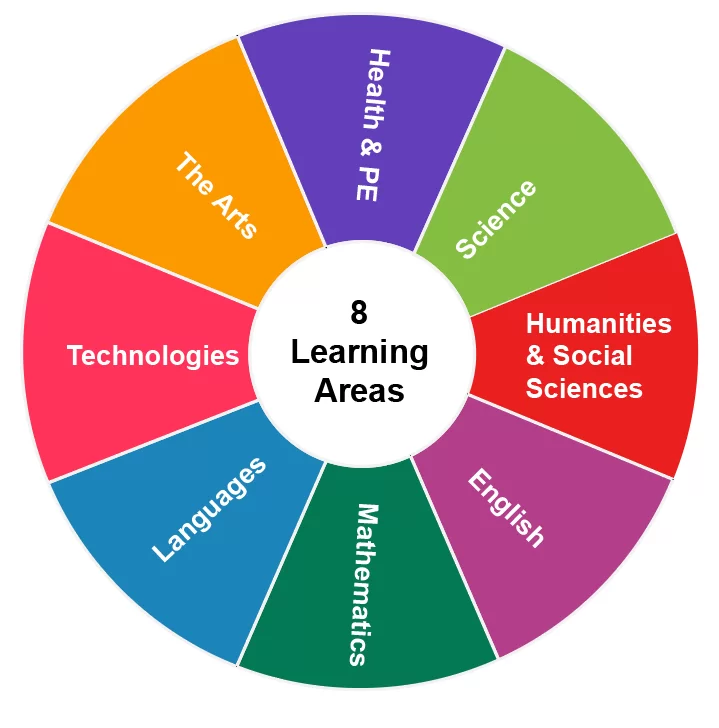
The Eight Key Learning Areas outline the specific knowledge that each student would gather in each subject area.
VCE and WACE Certifications in Australia
The Victorian Certificate of Education (VCE) and the Western Australian Certificate of Education (WACE) are certification programs in Australia that are awarded to students who complete their senior secondary education. However, these certificates are specific to the states of Victoria and Western Australia, respectively.
VCE (Victorian Certificate of Education)
The VCE is granted to the students who successfully complete their secondary education in the state of Victoria. The certificate is administered by the Victorian Curriculum and Assessment Authority (VCAA).
The VCE is undertaken over a two-year period in Years 11 and 12. When the students complete their schooling, they receive an Australian Tertiary Admission Rank (ATAR) based on their performance, which further helps them for university entrance purposes.
WACE (Western Australian Certificate of Education)
The WACE is granted to the students who successfully complete their secondary education in the states of Western Australia. This certificate is administered by the School Curriculum and Standards Authority (SCSA).
The WACE is undertaken over a period in Years 11 and 12. Unlike VCA, WACE candidates need to meet literacy and numeracy requirements and complete at least one senior secondary course examination. After their schooling, students receive ATAR based on their performance, which is used for further education and entrance in their preferred universities.
Australian Curriculum 9.0
The Australian Curriculum, Assessment and Reporting Authority (ACARA) released version 9.0 of the Australian Curriculum in May 2022. Schools have started implementing this new version in 2023 term 1.
Also read: Reassessing Curriculum Development: Top 3 Factors to Consider States and territories in the entire country have to adopt the updated version and introduce the students to version 9.0.

Version 9.0 of the Australian Curriculum offers a more practical approach for teachers regarding crucial knowledge that students must acquire
What Modifications have been Implemented in the Updated Curriculum?
The curriculum development in the updated version are decreased content, improved coordination between achievement standards and content descriptions, enhanced connections between learning areas, general capabilities, and cross-curriculum priorities.
The changes embraced by the updated curriculum are as follows:
- The Australian Curriculum is being modified to ensure a more thorough understanding and education, with a 21% reduction in descriptions regarding the learning objectives of students and what should be taught.
- There will be a greater emphasis on phonics in English and more focus on students mastering the fundamentals of mathematics, such as its different concepts, skills, and facts.
- The importance of developing proficiency in foundational skills and the ability to perform mathematical computations without a calculator will be emphasized.
- The sequencing of content in mathematics will be revised, particularly in areas such as telling time, introduction to fractions, recalling multiplication facts, and solving equations.
- Higher standards for mathematics will be set up for Year 1 regarding addition and subtraction and include multiplication facts in Year 2.
- In Years 9 and 10, priority will be given to Australian history, including the impact and perspectives of First Nation Australians upon the arrival of British settlers and their contributions to modern Australian society.
- ACARA is also working on mental health development among Australian youth. This will be taken into account in the upcoming versions of Australian Curriculum.

















